What does “PVC-Free” mean?

PVC-free fabrics are manufactured with virtually no harmful chemical content (these chemicals are called volatile organic compounds or VOCs). PVC fabrics can be recycled and are considered more environmentally friendly than other materials. PVC-free fabrics can contribute to improving the indoor air quality in a space, a priority or even a requirement for some projects. Some of these fabrics are also composed of post-consumer waste material, such as recycled water bottles.
While a PVC-free fabric offers many wonderful benefits, there are some advantages in selecting a PVC-coated fabric. PVC coating does increase strength, durability, and resistance-to-wear. It also enables fabrics to meet fire-resistance codes, achieve desired color properties, and improves resistance to damage from water, mildew, oils, and other chemicals.

PVC-free fabrics are manufactured with virtually no harmful chemical content (these chemicals are called volatile organic compounds or VOCs). PVC fabrics can be recycled and are considered more environmentally friendly than other materials. PVC-free fabrics can contribute to improving the indoor air quality in a space, a priority or even a requirement for some projects. Some of these fabrics are also composed of post-consumer waste material, such as recycled water bottles.
While a PVC-free fabric offers many wonderful benefits, there are some advantages in selecting a PVC-coated fabric. PVC coating does increase strength, durability, and resistance-to-wear. It also enables fabrics to meet fire-resistance codes, achieve desired color properties, and improves resistance to damage from water, mildew, oils, and other chemicals.

PVC-free fabrics are manufactured with virtually no harmful chemical content (these chemicals are called volatile organic compounds or VOCs). PVC fabrics can be recycled and are considered more environmentally friendly than other materials. PVC-free fabrics can contribute to improving the indoor air quality in a space, a priority or even a requirement for some projects. Some of these fabrics are also composed of post-consumer waste material, such as recycled water bottles.
While a PVC-free fabric offers many wonderful benefits, there are some advantages in selecting a PVC-coated fabric. PVC coating does increase strength, durability, and resistance-to-wear. It also enables fabrics to meet fire-resistance codes, achieve desired color properties, and improves resistance to damage from water, mildew, oils, and other chemicals.

PVC-free fabrics are manufactured with virtually no harmful chemical content (these chemicals are called volatile organic compounds or VOCs). PVC fabrics can be recycled and are considered more environmentally friendly than other materials. PVC-free fabrics can contribute to improving the indoor air quality in a space, a priority or even a requirement for some projects. Some of these fabrics are also composed of post-consumer waste material, such as recycled water bottles.
While a PVC-free fabric offers many wonderful benefits, there are some advantages in selecting a PVC-coated fabric. PVC coating does increase strength, durability, and resistance-to-wear. It also enables fabrics to meet fire-resistance codes, achieve desired color properties, and improves resistance to damage from water, mildew, oils, and other chemicals.

PVC-free fabrics are manufactured with virtually no harmful chemical content (these chemicals are called volatile organic compounds or VOCs). PVC fabrics can be recycled and are considered more environmentally friendly than other materials. PVC-free fabrics can contribute to improving the indoor air quality in a space, a priority or even a requirement for some projects. Some of these fabrics are also composed of post-consumer waste material, such as recycled water bottles.
While a PVC-free fabric offers many wonderful benefits, there are some advantages in selecting a PVC-coated fabric. PVC coating does increase strength, durability, and resistance-to-wear. It also enables fabrics to meet fire-resistance codes, achieve desired color properties, and improves resistance to damage from water, mildew, oils, and other chemicals.
What can automated shades do for my space?

Automated shades can make any space more comfortable and energy-efficient. With over 20 years of experience and knowledge in the automated shading industry, Lutron is the world leader in precision-controlled automated shades. Lutron also offers a wide variety of shading options, allowing you to create a cost-effective, environmentally-friendly, and aesthetically pleasing solution. Depending on the factors that are most important to you, you can select fabrics that increase daylight harvesting ability, reduce electric light consumption, minimize glare, enhance comfort, and improve productivity.
By maximizing energy efficiency, daylight and views, as well as incorporating environmentally-friendly materials, automated shades can help your building meet and exceed building codes and standards such as ASHRAE and LEED.

Automated shades can make any space more comfortable and energy-efficient. With over 20 years of experience and knowledge in the automated shading industry, Lutron is the world leader in precision-controlled automated shades. Lutron also offers a wide variety of shading options, allowing you to create a cost-effective, environmentally-friendly, and aesthetically pleasing solution. Depending on the factors that are most important to you, you can select fabrics that increase daylight harvesting ability, reduce electric light consumption, minimize glare, enhance comfort, and improve productivity.
By maximizing energy efficiency, daylight and views, as well as incorporating environmentally-friendly materials, automated shades can help your building meet and exceed building codes and standards such as ASHRAE and LEED.

Automated shades can make any space more comfortable and energy-efficient. With over 20 years of experience and knowledge in the automated shading industry, Lutron is the world leader in precision-controlled automated shades. Lutron also offers a wide variety of shading options, allowing you to create a cost-effective, environmentally-friendly, and aesthetically pleasing solution. Depending on the factors that are most important to you, you can select fabrics that increase daylight harvesting ability, reduce electric light consumption, minimize glare, enhance comfort, and improve productivity.
By maximizing energy efficiency, daylight and views, as well as incorporating environmentally-friendly materials, automated shades can help your building meet and exceed building codes and standards such as ASHRAE and LEED.

Automated shades can make any space more comfortable and energy-efficient. With over 20 years of experience and knowledge in the automated shading industry, Lutron is the world leader in precision-controlled automated shades. Lutron also offers a wide variety of shading options, allowing you to create a cost-effective, environmentally-friendly, and aesthetically pleasing solution. Depending on the factors that are most important to you, you can select fabrics that increase daylight harvesting ability, reduce electric light consumption, minimize glare, enhance comfort, and improve productivity.
By maximizing energy efficiency, daylight and views, as well as incorporating environmentally-friendly materials, automated shades can help your building meet and exceed building codes and standards such as ASHRAE and LEED.

Automated shades can make any space more comfortable and energy-efficient. With over 20 years of experience and knowledge in the automated shading industry, Lutron is the world leader in precision-controlled automated shades. Lutron also offers a wide variety of shading options, allowing you to create a cost-effective, environmentally-friendly, and aesthetically pleasing solution. Depending on the factors that are most important to you, you can select fabrics that increase daylight harvesting ability, reduce electric light consumption, minimize glare, enhance comfort, and improve productivity.
By maximizing energy efficiency, daylight and views, as well as incorporating environmentally-friendly materials, automated shades can help your building meet and exceed building codes and standards such as ASHRAE and LEED.
What is the difference between various fabric compositions?

Fabrics are made using many different materials to suit different purposes. Here are a few of the most commonly used fabric materials.
PVC-coated fiberglass - This lightweight, strong material serves as a good insulator and doesn’t stretch over time. PVC coating adds strength and durability, but cannot typically be recycled.
PVC-coated polyester - Comparably durable to PVC-coated fiberglass, the yarn core in polyester can be melted to make a clean-cut edge resulting in better edge-quality.
100% polyester - These fabrics are made with virtually no harmful chemical content (PVC-free). Polyester fabrics can be recycled and are considered more environmentally friendly than other fabric types. Polyester does tend to stretch over time – most vendors pre-stretch the fabric to minimize elongation of the shade.
Thermoplastic Olefin (TPO) - Designed to be tough and durable like polyester, TPO fabrics are made with virtually no harmful chemical content, allowing them to often be recyclable. TPOs have additional chemicals to meet fire-retardancy requirements and have relatively poor wear resistance over time.

Fabrics are made using many different materials to suit different purposes. Here are a few of the most commonly used fabric materials.
PVC-coated fiberglass - This lightweight, strong material serves as a good insulator and doesn’t stretch over time. PVC coating adds strength and durability, but cannot typically be recycled.
PVC-coated polyester - Comparably durable to PVC-coated fiberglass, the yarn core in polyester can be melted to make a clean-cut edge resulting in better edge-quality.
100% polyester - These fabrics are made with virtually no harmful chemical content (PVC-free). Polyester fabrics can be recycled and are considered more environmentally friendly than other fabric types. Polyester does tend to stretch over time – most vendors pre-stretch the fabric to minimize elongation of the shade.
Thermoplastic Olefin (TPO) - Designed to be tough and durable like polyester, TPO fabrics are made with virtually no harmful chemical content, allowing them to often be recyclable. TPOs have additional chemicals to meet fire-retardancy requirements and have relatively poor wear resistance over time.

Fabrics are made using many different materials to suit different purposes. Here are a few of the most commonly used fabric materials.
PVC-coated fiberglass - This lightweight, strong material serves as a good insulator and doesn’t stretch over time. PVC coating adds strength and durability, but cannot typically be recycled.
PVC-coated polyester - Comparably durable to PVC-coated fiberglass, the yarn core in polyester can be melted to make a clean-cut edge resulting in better edge-quality.
100% polyester - These fabrics are made with virtually no harmful chemical content (PVC-free). Polyester fabrics can be recycled and are considered more environmentally friendly than other fabric types. Polyester does tend to stretch over time – most vendors pre-stretch the fabric to minimize elongation of the shade.
Thermoplastic Olefin (TPO) - Designed to be tough and durable like polyester, TPO fabrics are made with virtually no harmful chemical content, allowing them to often be recyclable. TPOs have additional chemicals to meet fire-retardancy requirements and have relatively poor wear resistance over time.

Fabrics are made using many different materials to suit different purposes. Here are a few of the most commonly used fabric materials.
PVC-coated fiberglass - This lightweight, strong material serves as a good insulator and doesn’t stretch over time. PVC coating adds strength and durability, but cannot typically be recycled.
PVC-coated polyester - Comparably durable to PVC-coated fiberglass, the yarn core in polyester can be melted to make a clean-cut edge resulting in better edge-quality.
100% polyester - These fabrics are made with virtually no harmful chemical content (PVC-free). Polyester fabrics can be recycled and are considered more environmentally friendly than other fabric types. Polyester does tend to stretch over time – most vendors pre-stretch the fabric to minimize elongation of the shade.
Thermoplastic Olefin (TPO) - Designed to be tough and durable like polyester, TPO fabrics are made with virtually no harmful chemical content, allowing them to often be recyclable. TPOs have additional chemicals to meet fire-retardancy requirements and have relatively poor wear resistance over time.

Fabrics are made using many different materials to suit different purposes. Here are a few of the most commonly used fabric materials.
PVC-coated fiberglass - This lightweight, strong material serves as a good insulator and doesn’t stretch over time. PVC coating adds strength and durability, but cannot typically be recycled.
PVC-coated polyester - Comparably durable to PVC-coated fiberglass, the yarn core in polyester can be melted to make a clean-cut edge resulting in better edge-quality.
100% polyester - These fabrics are made with virtually no harmful chemical content (PVC-free). Polyester fabrics can be recycled and are considered more environmentally friendly than other fabric types. Polyester does tend to stretch over time – most vendors pre-stretch the fabric to minimize elongation of the shade.
Thermoplastic Olefin (TPO) - Designed to be tough and durable like polyester, TPO fabrics are made with virtually no harmful chemical content, allowing them to often be recyclable. TPOs have additional chemicals to meet fire-retardancy requirements and have relatively poor wear resistance over time.
What are the differences between the various weaves and knits available for fabrics?
Weaves
- Basketweave fabrics are woven on a loom by interlacing strands of yarn at right angles to each other. They are available in several varieties such as 1x1, 1x2 (e.g. Basketweave MS) and 2x2 (e.g. Basketweave 90).
In a twill weave fabric (e.g. Basketweave 27), the weave staggers warp and weft in order to produce a different look or pattern, and the diagonal is noticeable. A Jacquard weave is a much more intricate pattern, and is made on machines specifically dedicated to this type of weave. Jacquard-weave machines are very expensive but highly adaptable. This unique weave offers excellent room for creativity, and is ideal when a fabric requires a specific woven design.
Knits- Warp-knitted fabric (e.g. GreenScreen® Evolve™), is created by interlacing strands of yarn in a series of connected loops. Think of it as tying little loops into knots.

Weaves
- Basketweave fabrics are woven on a loom by interlacing strands of yarn at right angles to each other. They are available in several varieties such as 1x1, 1x2 (e.g. Basketweave MS) and 2x2 (e.g. Basketweave 90).
In a twill weave fabric (e.g. Basketweave 27), the weave staggers warp and weft in order to produce a different look or pattern, and the diagonal is noticeable. A Jacquard weave is a much more intricate pattern, and is made on machines specifically dedicated to this type of weave. Jacquard-weave machines are very expensive but highly adaptable. This unique weave offers excellent room for creativity, and is ideal when a fabric requires a specific woven design.
Knits- Warp-knitted fabric (e.g. GreenScreen® Evolve™), is created by interlacing strands of yarn in a series of connected loops. Think of it as tying little loops into knots.

Weaves
- Basketweave fabrics are woven on a loom by interlacing strands of yarn at right angles to each other. They are available in several varieties such as 1x1, 1x2 (e.g. Basketweave MS) and 2x2 (e.g. Basketweave 90).
In a twill weave fabric (e.g. Basketweave 27), the weave staggers warp and weft in order to produce a different look or pattern, and the diagonal is noticeable. A Jacquard weave is a much more intricate pattern, and is made on machines specifically dedicated to this type of weave. Jacquard-weave machines are very expensive but highly adaptable. This unique weave offers excellent room for creativity, and is ideal when a fabric requires a specific woven design.
Knits- Warp-knitted fabric (e.g. GreenScreen® Evolve™), is created by interlacing strands of yarn in a series of connected loops. Think of it as tying little loops into knots.

Weaves
- Basketweave fabrics are woven on a loom by interlacing strands of yarn at right angles to each other. They are available in several varieties such as 1x1, 1x2 (e.g. Basketweave MS) and 2x2 (e.g. Basketweave 90).
In a twill weave fabric (e.g. Basketweave 27), the weave staggers warp and weft in order to produce a different look or pattern, and the diagonal is noticeable. A Jacquard weave is a much more intricate pattern, and is made on machines specifically dedicated to this type of weave. Jacquard-weave machines are very expensive but highly adaptable. This unique weave offers excellent room for creativity, and is ideal when a fabric requires a specific woven design.
Knits- Warp-knitted fabric (e.g. GreenScreen® Evolve™), is created by interlacing strands of yarn in a series of connected loops. Think of it as tying little loops into knots.

Weaves
- Basketweave fabrics are woven on a loom by interlacing strands of yarn at right angles to each other. They are available in several varieties such as 1x1, 1x2 (e.g. Basketweave MS) and 2x2 (e.g. Basketweave 90).
In a twill weave fabric (e.g. Basketweave 27), the weave staggers warp and weft in order to produce a different look or pattern, and the diagonal is noticeable. A Jacquard weave is a much more intricate pattern, and is made on machines specifically dedicated to this type of weave. Jacquard-weave machines are very expensive but highly adaptable. This unique weave offers excellent room for creativity, and is ideal when a fabric requires a specific woven design.
Knits- Warp-knitted fabric (e.g. GreenScreen® Evolve™), is created by interlacing strands of yarn in a series of connected loops. Think of it as tying little loops into knots.
What are THEIA™ Compliant Fabrics?

THEIA™ Compliant Fabrics are certified, spec-grade fabrics that are compliant with the THEIA™ Performance Specification, which is a manufacturing specification for solar screen fabrics. By requiring tight manufacturing tolerances around fabric performance criteria, specifically openness factor and visible light transmittance, and defining the testing process and documentation, designers can be confident that the fabric delivered to the project will meet their design intent.
Today, the typical industry tolerances around fabric solar performance properties is large and can cause reduced visual comfort and energy savings. If fabric performance properties are not tightly controlled, your building design intent will not be achieved.
THEIA™ Compliant Fabrics:
- Are critical to ensure design intent for building performance is met
- Are held to a new standard to control variations in openness and transmittance
- Ensure that the fabric is delivered as specified.
Learn more about THEIA™ Compliant Fabrics at the Performance Shading Advisor.

THEIA™ Compliant Fabrics are certified, spec-grade fabrics that are compliant with the THEIA™ Performance Specification, which is a manufacturing specification for solar screen fabrics. By requiring tight manufacturing tolerances around fabric performance criteria, specifically openness factor and visible light transmittance, and defining the testing process and documentation, designers can be confident that the fabric delivered to the project will meet their design intent.
Today, the typical industry tolerances around fabric solar performance properties is large and can cause reduced visual comfort and energy savings. If fabric performance properties are not tightly controlled, your building design intent will not be achieved.
THEIA™ Compliant Fabrics:
- Are critical to ensure design intent for building performance is met
- Are held to a new standard to control variations in openness and transmittance
- Ensure that the fabric is delivered as specified.
Learn more about THEIA™ Compliant Fabrics at the Performance Shading Advisor.

THEIA™ Compliant Fabrics are certified, spec-grade fabrics that are compliant with the THEIA™ Performance Specification, which is a manufacturing specification for solar screen fabrics. By requiring tight manufacturing tolerances around fabric performance criteria, specifically openness factor and visible light transmittance, and defining the testing process and documentation, designers can be confident that the fabric delivered to the project will meet their design intent.
Today, the typical industry tolerances around fabric solar performance properties is large and can cause reduced visual comfort and energy savings. If fabric performance properties are not tightly controlled, your building design intent will not be achieved.
THEIA™ Compliant Fabrics:
- Are critical to ensure design intent for building performance is met
- Are held to a new standard to control variations in openness and transmittance
- Ensure that the fabric is delivered as specified.
Learn more about THEIA™ Compliant Fabrics at the Performance Shading Advisor.

THEIA™ Compliant Fabrics are certified, spec-grade fabrics that are compliant with the THEIA™ Performance Specification, which is a manufacturing specification for solar screen fabrics. By requiring tight manufacturing tolerances around fabric performance criteria, specifically openness factor and visible light transmittance, and defining the testing process and documentation, designers can be confident that the fabric delivered to the project will meet their design intent.
Today, the typical industry tolerances around fabric solar performance properties is large and can cause reduced visual comfort and energy savings. If fabric performance properties are not tightly controlled, your building design intent will not be achieved.
THEIA™ Compliant Fabrics:
- Are critical to ensure design intent for building performance is met
- Are held to a new standard to control variations in openness and transmittance
- Ensure that the fabric is delivered as specified.
Learn more about THEIA™ Compliant Fabrics at the Performance Shading Advisor.

THEIA™ Compliant Fabrics are certified, spec-grade fabrics that are compliant with the THEIA™ Performance Specification, which is a manufacturing specification for solar screen fabrics. By requiring tight manufacturing tolerances around fabric performance criteria, specifically openness factor and visible light transmittance, and defining the testing process and documentation, designers can be confident that the fabric delivered to the project will meet their design intent.
Today, the typical industry tolerances around fabric solar performance properties is large and can cause reduced visual comfort and energy savings. If fabric performance properties are not tightly controlled, your building design intent will not be achieved.
THEIA™ Compliant Fabrics:
- Are critical to ensure design intent for building performance is met
- Are held to a new standard to control variations in openness and transmittance
- Ensure that the fabric is delivered as specified.
Learn more about THEIA™ Compliant Fabrics at the Performance Shading Advisor.
Are certain fabrics better than others for railroading?

Railroading is an option for applications that require shades wider than the maximum usable width. It is critical to choose a fabric with good dimensional stability for railroading. Symmetrical weaves (1x1, 2x2, etc.) seem to perform best for railroading, and basketweave fabrics in particular have good dimensional stability.
Some examples of symmetrical weaves are
- Basketweave 90
- Basketweave E Screen
- SheerLite
- Basketweave 4000 Eco
- Basketweave Eco2

Railroading is an option for applications that require shades wider than the maximum usable width. It is critical to choose a fabric with good dimensional stability for railroading. Symmetrical weaves (1x1, 2x2, etc.) seem to perform best for railroading, and basketweave fabrics in particular have good dimensional stability.
Some examples of symmetrical weaves are
- Basketweave 90
- Basketweave E Screen
- SheerLite
- Basketweave 4000 Eco
- Basketweave Eco2

Railroading is an option for applications that require shades wider than the maximum usable width. It is critical to choose a fabric with good dimensional stability for railroading. Symmetrical weaves (1x1, 2x2, etc.) seem to perform best for railroading, and basketweave fabrics in particular have good dimensional stability.
Some examples of symmetrical weaves are
- Basketweave 90
- Basketweave E Screen
- SheerLite
- Basketweave 4000 Eco
- Basketweave Eco2

Railroading is an option for applications that require shades wider than the maximum usable width. It is critical to choose a fabric with good dimensional stability for railroading. Symmetrical weaves (1x1, 2x2, etc.) seem to perform best for railroading, and basketweave fabrics in particular have good dimensional stability.
Some examples of symmetrical weaves are
- Basketweave 90
- Basketweave E Screen
- SheerLite
- Basketweave 4000 Eco
- Basketweave Eco2

Railroading is an option for applications that require shades wider than the maximum usable width. It is critical to choose a fabric with good dimensional stability for railroading. Symmetrical weaves (1x1, 2x2, etc.) seem to perform best for railroading, and basketweave fabrics in particular have good dimensional stability.
Some examples of symmetrical weaves are
- Basketweave 90
- Basketweave E Screen
- SheerLite
- Basketweave 4000 Eco
- Basketweave Eco2
How can automated shades help my building or home be more energy efficient?
Automated shades allow you to maximize the amount of daylight entering a space, and can save energy by minimizing reliance on electric light.
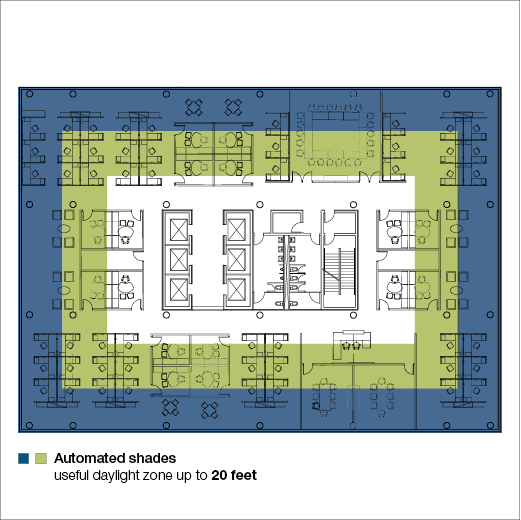
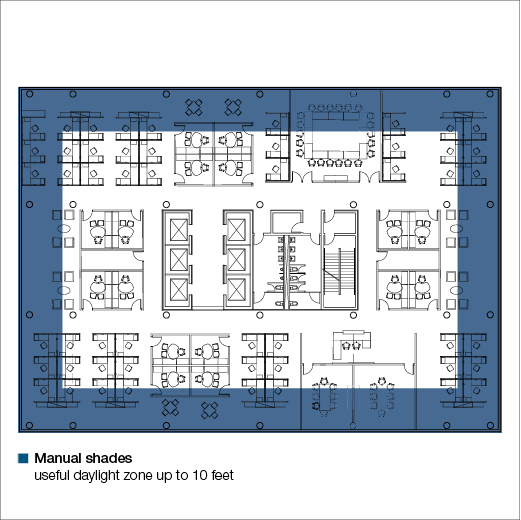
Lutron supports a new sustainability concept, Daylight Autonomy, which is the percentage of daytime hours that a significant amount of useful daylight is present in a space. It is known that automated shades enhance the useful daylight zone (the area inside a space illuminated by daylight). Manual shade applications typically extend the useful daylight zone about 10 feet inside the perimeter of a space while automated shades can extend that zone to 20 feet. Automated shades allow for higher daylight autonomy, since manual shades are rarely adjusted. This concept significantly enhances the energy saving potential of Lutron lighting systems through daylight harvesting.
The Daylight Autonomy value can be even higher by combining Sivoia® QS shades, Hyperion® solar-adaptive shading technology, the Radio Window Sensor, and Lutron’s daylight dimming technology. Utilizing these solutions together significantly increases the electricity savings in a space,while mitigating glare and improving occupant comfort and productivity. Other benefits include improved workplace aesthetics, and increased exposure today light and views (it is widely accepted that it improves overall health and well-being, attention to detail, and better stress management).
Watch the video to learn more about day light autonomy.
Automated shades allow you to maximize the amount of daylight entering a space, and can save energy by minimizing reliance on electric light.
Lutron supports a new sustainability concept, Daylight Autonomy, which is the percentage of daytime hours that a significant amount of useful daylight is present in a space. It is known that automated shades enhance the useful daylight zone (the area inside a space illuminated by daylight). Manual shade applications typically extend the useful daylight zone about 10 feet inside the perimeter of a space while automated shades can extend that zone to 20 feet. Automated shades allow for higher daylight autonomy, since manual shades are rarely adjusted. This concept significantly enhances the energy saving potential of Lutron lighting systems through daylight harvesting.
The Daylight Autonomy value can be even higher by combining Sivoia® QS shades, Hyperion® solar-adaptive shading technology, the Radio Window Sensor, and Lutron’s daylight dimming technology. Utilizing these solutions together significantly increases the electricity savings in a space,while mitigating glare and improving occupant comfort and productivity. Other benefits include improved workplace aesthetics, and increased exposure today light and views (it is widely accepted that it improves overall health and well-being, attention to detail, and better stress management).
Watch the video to learn more about day light autonomy.


Automated shades allow you to maximize the amount of daylight entering a space, and can save energy by minimizing reliance on electric light.
Lutron supports a new sustainability concept, Daylight Autonomy, which is the percentage of daytime hours that a significant amount of useful daylight is present in a space. It is known that automated shades enhance the useful daylight zone (the area inside a space illuminated by daylight). Manual shade applications typically extend the useful daylight zone about 10 feet inside the perimeter of a space while automated shades can extend that zone to 20 feet. Automated shades allow for higher daylight autonomy, since manual shades are rarely adjusted. This concept significantly enhances the energy saving potential of Lutron lighting systems through daylight harvesting.
The Daylight Autonomy value can be even higher by combining Sivoia® QS shades, Hyperion® solar-adaptive shading technology, the Radio Window Sensor, and Lutron’s daylight dimming technology. Utilizing these solutions together significantly increases the electricity savings in a space,while mitigating glare and improving occupant comfort and productivity. Other benefits include improved workplace aesthetics, and increased exposure today light and views (it is widely accepted that it improves overall health and well-being, attention to detail, and better stress management).
Watch the video to learn more about day light autonomy.


Automated shades allow you to maximize the amount of daylight entering a space, and can save energy by minimizing reliance on electric light.
Lutron supports a new sustainability concept, Daylight Autonomy, which is the percentage of daytime hours that a significant amount of useful daylight is present in a space. It is known that automated shades enhance the useful daylight zone (the area inside a space illuminated by daylight). Manual shade applications typically extend the useful daylight zone about 10 feet inside the perimeter of a space while automated shades can extend that zone to 20 feet. Automated shades allow for higher daylight autonomy, since manual shades are rarely adjusted. This concept significantly enhances the energy saving potential of Lutron lighting systems through daylight harvesting.
The Daylight Autonomy value can be even higher by combining Sivoia® QS shades, Hyperion® solar-adaptive shading technology, the Radio Window Sensor, and Lutron’s daylight dimming technology. Utilizing these solutions together significantly increases the electricity savings in a space,while mitigating glare and improving occupant comfort and productivity. Other benefits include improved workplace aesthetics, and increased exposure today light and views (it is widely accepted that it improves overall health and well-being, attention to detail, and better stress management).
Watch the video to learn more about day light autonomy.


Automated shades allow you to maximize the amount of daylight entering a space, and can save energy by minimizing reliance on electric light.
Lutron supports a new sustainability concept, Daylight Autonomy, which is the percentage of daytime hours that a significant amount of useful daylight is present in a space. It is known that automated shades enhance the useful daylight zone (the area inside a space illuminated by daylight). Manual shade applications typically extend the useful daylight zone about 10 feet inside the perimeter of a space while automated shades can extend that zone to 20 feet. Automated shades allow for higher daylight autonomy, since manual shades are rarely adjusted. This concept significantly enhances the energy saving potential of Lutron lighting systems through daylight harvesting.
The Daylight Autonomy value can be even higher by combining Sivoia® QS shades, Hyperion® solar-adaptive shading technology, the Radio Window Sensor, and Lutron’s daylight dimming technology. Utilizing these solutions together significantly increases the electricity savings in a space,while mitigating glare and improving occupant comfort and productivity. Other benefits include improved workplace aesthetics, and increased exposure today light and views (it is widely accepted that it improves overall health and well-being, attention to detail, and better stress management).
Watch the video to learn more about day light autonomy.


Shade Terminology – What keywords are helpful to know?

Dual-sided - Some fabrics have two different properties (most noticeably color) that meet two different needs –one for the side facing the exterior and one facing the interior.
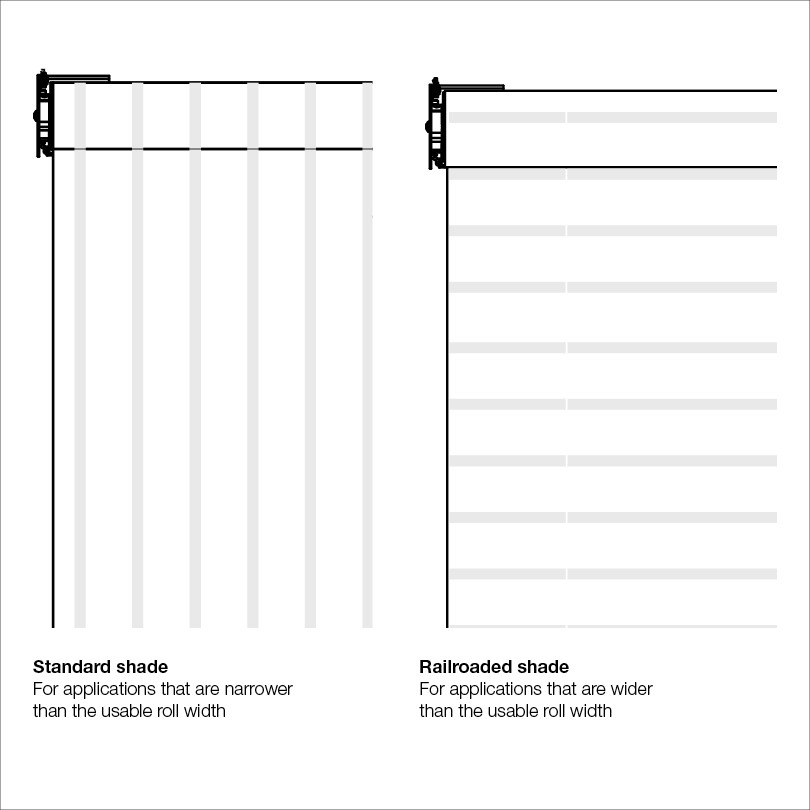
Maximum Usable Width - Each roll of fabric has a maximum width based on the size of the loom on which the fabric is constructed. In some cases, railroading a fabric can provide a solution for wide shades.
Openness Factor - Openness factor describes the ratio of open space to fabric material. Simply stated, it measures how tightly fabrics are woven – the tighter the weave, the less daylight filters through. There are typically three types of fabrics classified by openness factor – Sheer, Translucent/Dim-out, or Blackout fabrics. Sheer fabrics have a high transparency, and the openness factor is 1% or higher. Common openness factors for sheer shades are 1%, 3%, 5%, and 10%. These fabrics allow more daylight to enter a space for a better view outside.
Translucent or Dim-out fabrics, also referred to as privacy fabrics, have an openness factor between 0% and 1%. These fabrics let in a limited amount of daylight. A view outside will have very little detail – you will only see shapes and shadows.
Blackout fabrics, or opaque fabrics, have a 0% openness factor and block 100% of daylight. Commercially, blackout fabrics are often used in conference room applications to allow for presentations or videoconferences. For total blackout, a side channel is required.



PVC-freePVC-free - fabrics have virtually no harmful chemical content (known as VOCs), allowing them to be recycled and are considered more environmentally friendly than other fabric types.
Railroading - Railroading fabric is an option for applications requiring shades wider than the maximum usable width. Railroading rotates the fabric 90 degrees from its typical orientation. If the fabric has a distinct pattern, please note that this pattern will also be rotated 90 degrees, thereby altering the final appearance of the shade. Railroading is best done with a symmetrical weave fabric.


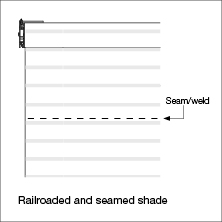
Seamable - Some fabrics can be seamed/welded together in order to increase the size of a railroaded shade beyond its fabric roll width. This technique issued to achieve long, wide shades. If a fabric has a distinct pattern, aligning the pattern during seaming may alter the final appearance of the shade.
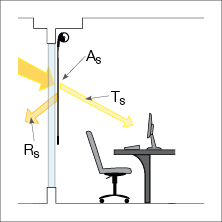

Total Radiation (Ts + Rs+ As = Total Radiation) - Total Radiation is measured as a combination of three other values – Solar Transmittance, Solar Reflectance and Solar Absorption. These three values always add up to 100, or Total Radiation.
Solar Transmittance (Ts) - the percentage of total radiation transmitted through the fabric. A lower figure indicates good filtration of solar energy and light.
Solar Reflectance (Rs) - the percentage of total radiation reflected by the fabric. A higher figure is good for controlling heat gain (for internal applications).
Solar Absorption (As) - the percentage of total radiation absorbed by the fabric. A lower figure indicates a low absorption of solar energy.
Visual Transmittance (Tv) - The Tv value is the percentage of visible light transmission through the fabric. This is an important measurement for understanding how a shade will help to minimize glare and visual comfort. Typically, a high Tv value can indicate high glare.
Volatile Organic Compound (VOC) - Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are organic chemicals that have a high vapor pressure at ordinary room-temperature conditions. Most scents or odors indicate the presence of VOCs. VOCs that are considered harmful aren’t typically acutely toxic, but research shows they can have longer-term health effects.
Greenguard® certification - means a product has passed testing for indoor pollutant emissions and can be considered low-VOC
Visual Transmittance (Tv) - The Tv value is the percentage of visible light transmission through the fabric. This is an important measurement for understanding how a shade will help to minimize glare and visual comfort. Typically, a high Tv value can indicate high glare.

Dual-sided - Some fabrics have two different properties (most noticeably color) that meet two different needs –one for the side facing the exterior and one facing the interior.
Maximum Usable Width - Each roll of fabric has a maximum width based on the size of the loom on which the fabric is constructed. In some cases, railroading a fabric can provide a solution for wide shades.
Openness Factor - Openness factor describes the ratio of open space to fabric material. Simply stated, it measures how tightly fabrics are woven – the tighter the weave, the less daylight filters through. There are typically three types of fabrics classified by openness factor – Sheer, Translucent/Dim-out, or Blackout fabrics. Sheer fabrics have a high transparency, and the openness factor is 1% or higher. Common openness factors for sheer shades are 1%, 3%, 5%, and 10%. These fabrics allow more daylight to enter a space for a better view outside.

Dual-sided - Some fabrics have two different properties (most noticeably color) that meet two different needs –one for the side facing the exterior and one facing the interior.
Maximum Usable Width - Each roll of fabric has a maximum width based on the size of the loom on which the fabric is constructed. In some cases, railroading a fabric can provide a solution for wide shades.
Openness Factor - Openness factor describes the ratio of open space to fabric material. Simply stated, it measures how tightly fabrics are woven – the tighter the weave, the less daylight filters through. There are typically three types of fabrics classified by openness factor – Sheer, Translucent/Dim-out, or Blackout fabrics. Sheer fabrics have a high transparency, and the openness factor is 1% or higher. Common openness factors for sheer shades are 1%, 3%, 5%, and 10%. These fabrics allow more daylight to enter a space for a better view outside.
Translucent or Dim-out fabrics, also referred to as privacy fabrics, have an openness factor between 0% and 1%. These fabrics let in a limited amount of daylight. A view outside will have very little detail – you will only see shapes and shadows.
Blackout fabrics, or opaque fabrics, have a 0% openness factor and block 100% of daylight. Commercially, blackout fabrics are often used in conference room applications to allow for presentations or videoconferences. For total blackout, a side channel is required.
Translucent or Dim-out fabrics, also referred to as privacy fabrics, have an openness factor between 0% and 1%. These fabrics let in a limited amount of daylight. A view outside will have very little detail – you will only see shapes and shadows.
Blackout fabrics, or opaque fabrics, have a 0% openness factor and block 100% of daylight. Commercially, blackout fabrics are often used in conference room applications to allow for presentations or videoconferences. For total blackout, a side channel is required.






PVC-freePVC-free - fabrics have virtually no harmful chemical content (known as VOCs), allowing them to be recycled and are considered more environmentally friendly than other fabric types.
Railroading - Railroading fabric is an option for applications requiring shades wider than the maximum usable width. Railroading rotates the fabric 90 degrees from its typical orientation. If the fabric has a distinct pattern, please note that this pattern will also be rotated 90 degrees, thereby altering the final appearance of the shade. Railroading is best done with a symmetrical weave fabric.
PVC-freePVC-free - fabrics have virtually no harmful chemical content (known as VOCs), allowing them to be recycled and are considered more environmentally friendly than other fabric types.
Railroading - Railroading fabric is an option for applications requiring shades wider than the maximum usable width. Railroading rotates the fabric 90 degrees from its typical orientation. If the fabric has a distinct pattern, please note that this pattern will also be rotated 90 degrees, thereby altering the final appearance of the shade. Railroading is best done with a symmetrical weave fabric.






Seamable - Some fabrics can be seamed/welded together in order to increase the size of a railroaded shade beyond its fabric roll width. This technique issued to achieve long, wide shades. If a fabric has a distinct pattern, aligning the pattern during seaming may alter the final appearance of the shade.
Seamable - Some fabrics can be seamed/welded together in order to increase the size of a railroaded shade beyond its fabric roll width. This technique issued to achieve long, wide shades. If a fabric has a distinct pattern, aligning the pattern during seaming may alter the final appearance of the shade.


Total Radiation (Ts + Rs+ As = Total Radiation) - Total Radiation is measured as a combination of three other values – Solar Transmittance, Solar Reflectance and Solar Absorption. These three values always add up to 100, or Total Radiation.
Solar Transmittance (Ts) - the percentage of total radiation transmitted through the fabric. A lower figure indicates good filtration of solar energy and light.
Solar Reflectance (Rs) - the percentage of total radiation reflected by the fabric. A higher figure is good for controlling heat gain (for internal applications).
Solar Absorption (As) - the percentage of total radiation absorbed by the fabric. A lower figure indicates a low absorption of solar energy.
Visual Transmittance (Tv) - The Tv value is the percentage of visible light transmission through the fabric. This is an important measurement for understanding how a shade will help to minimize glare and visual comfort. Typically, a high Tv value can indicate high glare.
Volatile Organic Compound (VOC) - Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are organic chemicals that have a high vapor pressure at ordinary room-temperature conditions. Most scents or odors indicate the presence of VOCs. VOCs that are considered harmful aren’t typically acutely toxic, but research shows they can have longer-term health effects.
Greenguard® certification - means a product has passed testing for indoor pollutant emissions and can be considered low-VOC


Total Radiation (Ts + Rs+ As = Total Radiation) - Total Radiation is measured as a combination of three other values – Solar Transmittance, Solar Reflectance and Solar Absorption. These three values always add up to 100, or Total Radiation.
Solar Transmittance (Ts) - the percentage of total radiation transmitted through the fabric. A lower figure indicates good filtration of solar energy and light.
Solar Reflectance (Rs) - the percentage of total radiation reflected by the fabric. A higher figure is good for controlling heat gain (for internal applications).
Solar Absorption (As) - the percentage of total radiation absorbed by the fabric. A lower figure indicates a low absorption of solar energy.
Visual Transmittance (Tv) - The Tv value is the percentage of visible light transmission through the fabric. This is an important measurement for understanding how a shade will help to minimize glare and visual comfort. Typically, a high Tv value can indicate high glare.
Volatile Organic Compound (VOC) - Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are organic chemicals that have a high vapor pressure at ordinary room-temperature conditions. Most scents or odors indicate the presence of VOCs. VOCs that are considered harmful aren’t typically acutely toxic, but research shows they can have longer-term health effects.
Greenguard® certification - means a product has passed testing for indoor pollutant emissions and can be considered low-VOC
Visual Transmittance (Tv) - The Tv value is the percentage of visible light transmission through the fabric. This is an important measurement for understanding how a shade will help to minimize glare and visual comfort. Typically, a high Tv value can indicate high glare.

Dual-sided - Some fabrics have two different properties (most noticeably color) that meet two different needs –one for the side facing the exterior and one facing the interior.
Maximum Usable Width - Each roll of fabric has a maximum width based on the size of the loom on which the fabric is constructed. In some cases, railroading a fabric can provide a solution for wide shades.
Openness Factor - Openness factor describes the ratio of open space to fabric material. Simply stated, it measures how tightly fabrics are woven – the tighter the weave, the less daylight filters through. There are typically three types of fabrics classified by openness factor – Sheer, Translucent/Dim-out, or Blackout fabrics. Sheer fabrics have a high transparency, and the openness factor is 1% or higher. Common openness factors for sheer shades are 1%, 3%, 5%, and 10%. These fabrics allow more daylight to enter a space for a better view outside.

Dual-sided - Some fabrics have two different properties (most noticeably color) that meet two different needs –one for the side facing the exterior and one facing the interior.
Maximum Usable Width - Each roll of fabric has a maximum width based on the size of the loom on which the fabric is constructed. In some cases, railroading a fabric can provide a solution for wide shades.
Openness Factor - Openness factor describes the ratio of open space to fabric material. Simply stated, it measures how tightly fabrics are woven – the tighter the weave, the less daylight filters through. There are typically three types of fabrics classified by openness factor – Sheer, Translucent/Dim-out, or Blackout fabrics. Sheer fabrics have a high transparency, and the openness factor is 1% or higher. Common openness factors for sheer shades are 1%, 3%, 5%, and 10%. These fabrics allow more daylight to enter a space for a better view outside.
Translucent or Dim-out fabrics, also referred to as privacy fabrics, have an openness factor between 0% and 1%. These fabrics let in a limited amount of daylight. A view outside will have very little detail – you will only see shapes and shadows.
Blackout fabrics, or opaque fabrics, have a 0% openness factor and block 100% of daylight. Commercially, blackout fabrics are often used in conference room applications to allow for presentations or videoconferences. For total blackout, a side channel is required.
Translucent or Dim-out fabrics, also referred to as privacy fabrics, have an openness factor between 0% and 1%. These fabrics let in a limited amount of daylight. A view outside will have very little detail – you will only see shapes and shadows.
Blackout fabrics, or opaque fabrics, have a 0% openness factor and block 100% of daylight. Commercially, blackout fabrics are often used in conference room applications to allow for presentations or videoconferences. For total blackout, a side channel is required.






PVC-freePVC-free - fabrics have virtually no harmful chemical content (known as VOCs), allowing them to be recycled and are considered more environmentally friendly than other fabric types.
Railroading - Railroading fabric is an option for applications requiring shades wider than the maximum usable width. Railroading rotates the fabric 90 degrees from its typical orientation. If the fabric has a distinct pattern, please note that this pattern will also be rotated 90 degrees, thereby altering the final appearance of the shade. Railroading is best done with a symmetrical weave fabric.
PVC-freePVC-free - fabrics have virtually no harmful chemical content (known as VOCs), allowing them to be recycled and are considered more environmentally friendly than other fabric types.
Railroading - Railroading fabric is an option for applications requiring shades wider than the maximum usable width. Railroading rotates the fabric 90 degrees from its typical orientation. If the fabric has a distinct pattern, please note that this pattern will also be rotated 90 degrees, thereby altering the final appearance of the shade. Railroading is best done with a symmetrical weave fabric.






Seamable - Some fabrics can be seamed/welded together in order to increase the size of a railroaded shade beyond its fabric roll width. This technique issued to achieve long, wide shades. If a fabric has a distinct pattern, aligning the pattern during seaming may alter the final appearance of the shade.
Seamable - Some fabrics can be seamed/welded together in order to increase the size of a railroaded shade beyond its fabric roll width. This technique issued to achieve long, wide shades. If a fabric has a distinct pattern, aligning the pattern during seaming may alter the final appearance of the shade.


Total Radiation (Ts + Rs+ As = Total Radiation) - Total Radiation is measured as a combination of three other values – Solar Transmittance, Solar Reflectance and Solar Absorption. These three values always add up to 100, or Total Radiation.
Solar Transmittance (Ts) - the percentage of total radiation transmitted through the fabric. A lower figure indicates good filtration of solar energy and light.
Solar Reflectance (Rs) - the percentage of total radiation reflected by the fabric. A higher figure is good for controlling heat gain (for internal applications).
Solar Absorption (As) - the percentage of total radiation absorbed by the fabric. A lower figure indicates a low absorption of solar energy.
Visual Transmittance (Tv) - The Tv value is the percentage of visible light transmission through the fabric. This is an important measurement for understanding how a shade will help to minimize glare and visual comfort. Typically, a high Tv value can indicate high glare.
Volatile Organic Compound (VOC) - Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are organic chemicals that have a high vapor pressure at ordinary room-temperature conditions. Most scents or odors indicate the presence of VOCs. VOCs that are considered harmful aren’t typically acutely toxic, but research shows they can have longer-term health effects.
Greenguard® certification - means a product has passed testing for indoor pollutant emissions and can be considered low-VOC


Total Radiation (Ts + Rs+ As = Total Radiation) - Total Radiation is measured as a combination of three other values – Solar Transmittance, Solar Reflectance and Solar Absorption. These three values always add up to 100, or Total Radiation.
Solar Transmittance (Ts) - the percentage of total radiation transmitted through the fabric. A lower figure indicates good filtration of solar energy and light.
Solar Reflectance (Rs) - the percentage of total radiation reflected by the fabric. A higher figure is good for controlling heat gain (for internal applications).
Solar Absorption (As) - the percentage of total radiation absorbed by the fabric. A lower figure indicates a low absorption of solar energy.
Visual Transmittance (Tv) - The Tv value is the percentage of visible light transmission through the fabric. This is an important measurement for understanding how a shade will help to minimize glare and visual comfort. Typically, a high Tv value can indicate high glare.
Volatile Organic Compound (VOC) - Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are organic chemicals that have a high vapor pressure at ordinary room-temperature conditions. Most scents or odors indicate the presence of VOCs. VOCs that are considered harmful aren’t typically acutely toxic, but research shows they can have longer-term health effects.
Greenguard® certification - means a product has passed testing for indoor pollutant emissions and can be considered low-VOC
Visual Transmittance (Tv) - The Tv value is the percentage of visible light transmission through the fabric. This is an important measurement for understanding how a shade will help to minimize glare and visual comfort. Typically, a high Tv value can indicate high glare.
Are different fabrics better than others for reducing glare?
Understanding Tv value is essential to reducing glare and improving visual comfort. Tv is the percentage of visible light, as opposed to total solar radiation, that is transmitted through the shade. Typically, a high Tv value in a fabric can lead to higher possibility for glare and visual discomfort.
Like transmittance, reflectance, and absorption, there is a Tv value for all materials, and Tv is additive. To be most effective, you should consider the Tv value of the window glazing before selecting a fabric.
A typical Tv value for windows in new construction is 70-80%. You don’t want to block all visible light entering the space, so choose a fabric with a low Tv value for the shade.
Inversely, if your glass is tinted, the Tv value and amount of visible light will be lower (40-50%). In this case, your fabric’s Tv value may not need to be as low, since the glass is helping to reduce glare.
Understanding Tv value is essential to reducing glare and improving visual comfort. Tv is the percentage of visible light, as opposed to total solar radiation, that is transmitted through the shade. Typically, a high Tv value in a fabric can lead to higher possibility for glare and visual discomfort.
Like transmittance, reflectance, and absorption, there is a Tv value for all materials, and Tv is additive. To be most effective, you should consider the Tv value of the window glazing before selecting a fabric.
A typical Tv value for windows in new construction is 70-80%. You don’t want to block all visible light entering the space, so choose a fabric with a low Tv value for the shade.
Inversely, if your glass is tinted, the Tv value and amount of visible light will be lower (40-50%). In this case, your fabric’s Tv value may not need to be as low, since the glass is helping to reduce glare.
Understanding Tv value is essential to reducing glare and improving visual comfort. Tv is the percentage of visible light, as opposed to total solar radiation, that is transmitted through the shade. Typically, a high Tv value in a fabric can lead to higher possibility for glare and visual discomfort.
Like transmittance, reflectance, and absorption, there is a Tv value for all materials, and Tv is additive. To be most effective, you should consider the Tv value of the window glazing before selecting a fabric.
A typical Tv value for windows in new construction is 70-80%. You don’t want to block all visible light entering the space, so choose a fabric with a low Tv value for the shade.
Inversely, if your glass is tinted, the Tv value and amount of visible light will be lower (40-50%). In this case, your fabric’s Tv value may not need to be as low, since the glass is helping to reduce glare.




Understanding Tv value is essential to reducing glare and improving visual comfort. Tv is the percentage of visible light, as opposed to total solar radiation, that is transmitted through the shade. Typically, a high Tv value in a fabric can lead to higher possibility for glare and visual discomfort.
Like transmittance, reflectance, and absorption, there is a Tv value for all materials, and Tv is additive. To be most effective, you should consider the Tv value of the window glazing before selecting a fabric.
A typical Tv value for windows in new construction is 70-80%. You don’t want to block all visible light entering the space, so choose a fabric with a low Tv value for the shade.
Inversely, if your glass is tinted, the Tv value and amount of visible light will be lower (40-50%). In this case, your fabric’s Tv value may not need to be as low, since the glass is helping to reduce glare.
Understanding Tv value is essential to reducing glare and improving visual comfort. Tv is the percentage of visible light, as opposed to total solar radiation, that is transmitted through the shade. Typically, a high Tv value in a fabric can lead to higher possibility for glare and visual discomfort.
Like transmittance, reflectance, and absorption, there is a Tv value for all materials, and Tv is additive. To be most effective, you should consider the Tv value of the window glazing before selecting a fabric.
A typical Tv value for windows in new construction is 70-80%. You don’t want to block all visible light entering the space, so choose a fabric with a low Tv value for the shade.
Inversely, if your glass is tinted, the Tv value and amount of visible light will be lower (40-50%). In this case, your fabric’s Tv value may not need to be as low, since the glass is helping to reduce glare.




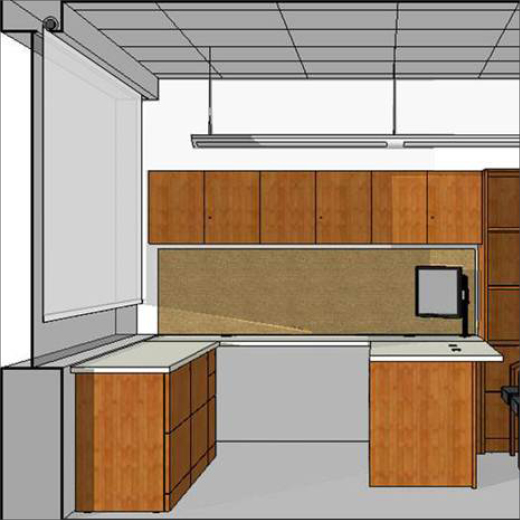
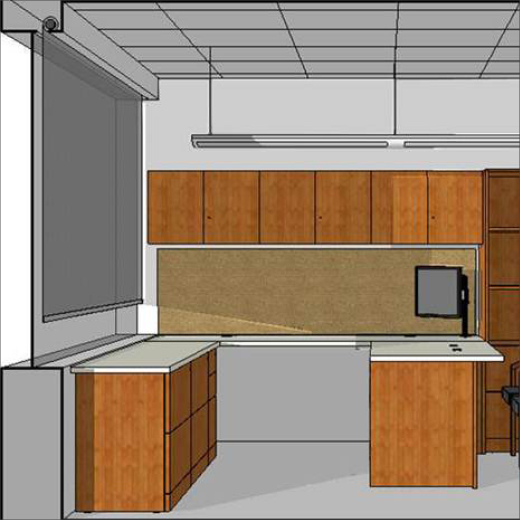
How does the color of the fabric affect views and heat?
Light and dark fabrics have advantages and disadvantages, depending on their application. The ideal fabric color can vary by project based on location, orientation, design aesthetics, or project priorities such as whether a space requires glare control.
Lighter colored fabrics are advantageous in indirect light environments. They can reflect a higher percentage of solar radiation to help block more heat and light, while preserving levels of daylight and reducing the need for electric light.
As shown in this image however, outside views are actually less clear with light-colored fabrics because they cause interior light to be reflected back into the space. Direct light through a light-colored fabric can also cause higher glare and more visual discomfort.
A darker fabric will have a lower Tv value, which means reduced glare. A darker fabric will also blend with the glass, appear more transparent than a lighter fabric and provide a better view.Think of a darker shade like wearing polarized sunglasses, where the intensity of the light is masked but the view is still clear. There is a common perception that a darker fabric means increased heat gain, since darker colors will absorb more solar heat than lighter colors. There is some truth to this inter ms of the shade, however in most contemporary buildings, the glazing system is very efficient at insulating the interior space.



Light and dark fabrics have advantages and disadvantages, depending on their application. The ideal fabric color can vary by project based on location, orientation, design aesthetics, or project priorities such as whether a space requires glare control.
Lighter colored fabrics are advantageous in indirect light environments. They can reflect a higher percentage of solar radiation to help block more heat and light, while preserving levels of daylight and reducing the need for electric light.
As shown in this image however, outside views are actually less clear with light-colored fabrics because they cause interior light to be reflected back into the space. Direct light through a light-colored fabric can also cause higher glare and more visual discomfort.
A darker fabric will have a lower Tv value, which means reduced glare. A darker fabric will also blend with the glass, appear more transparent than a lighter fabric and provide a better view.Think of a darker shade like wearing polarized sunglasses, where the intensity of the light is masked but the view is still clear. There is a common perception that a darker fabric means increased heat gain, since darker colors will absorb more solar heat than lighter colors. There is some truth to this inter ms of the shade, however in most contemporary buildings, the glazing system is very efficient at insulating the interior space.
Light and dark fabrics have advantages and disadvantages, depending on their application. The ideal fabric color can vary by project based on location, orientation, design aesthetics, or project priorities such as whether a space requires glare control.
Lighter colored fabrics are advantageous in indirect light environments. They can reflect a higher percentage of solar radiation to help block more heat and light, while preserving levels of daylight and reducing the need for electric light.
As shown in this image however, outside views are actually less clear with light-colored fabrics because they cause interior light to be reflected back into the space. Direct light through a light-colored fabric can also cause higher glare and more visual discomfort.
A darker fabric will have a lower Tv value, which means reduced glare. A darker fabric will also blend with the glass, appear more transparent than a lighter fabric and provide a better view.Think of a darker shade like wearing polarized sunglasses, where the intensity of the light is masked but the view is still clear. There is a common perception that a darker fabric means increased heat gain, since darker colors will absorb more solar heat than lighter colors. There is some truth to this inter ms of the shade, however in most contemporary buildings, the glazing system is very efficient at insulating the interior space.






Light and dark fabrics have advantages and disadvantages, depending on their application. The ideal fabric color can vary by project based on location, orientation, design aesthetics, or project priorities such as whether a space requires glare control.
Lighter colored fabrics are advantageous in indirect light environments. They can reflect a higher percentage of solar radiation to help block more heat and light, while preserving levels of daylight and reducing the need for electric light.
As shown in this image however, outside views are actually less clear with light-colored fabrics because they cause interior light to be reflected back into the space. Direct light through a light-colored fabric can also cause higher glare and more visual discomfort.
A darker fabric will have a lower Tv value, which means reduced glare. A darker fabric will also blend with the glass, appear more transparent than a lighter fabric and provide a better view.Think of a darker shade like wearing polarized sunglasses, where the intensity of the light is masked but the view is still clear. There is a common perception that a darker fabric means increased heat gain, since darker colors will absorb more solar heat than lighter colors. There is some truth to this inter ms of the shade, however in most contemporary buildings, the glazing system is very efficient at insulating the interior space.
Light and dark fabrics have advantages and disadvantages, depending on their application. The ideal fabric color can vary by project based on location, orientation, design aesthetics, or project priorities such as whether a space requires glare control.
Lighter colored fabrics are advantageous in indirect light environments. They can reflect a higher percentage of solar radiation to help block more heat and light, while preserving levels of daylight and reducing the need for electric light.
As shown in this image however, outside views are actually less clear with light-colored fabrics because they cause interior light to be reflected back into the space. Direct light through a light-colored fabric can also cause higher glare and more visual discomfort.
A darker fabric will have a lower Tv value, which means reduced glare. A darker fabric will also blend with the glass, appear more transparent than a lighter fabric and provide a better view.Think of a darker shade like wearing polarized sunglasses, where the intensity of the light is masked but the view is still clear. There is a common perception that a darker fabric means increased heat gain, since darker colors will absorb more solar heat than lighter colors. There is some truth to this inter ms of the shade, however in most contemporary buildings, the glazing system is very efficient at insulating the interior space.






What fabric certifications and standards should I consider?
In today’s buildings, products and materials must meet certain standards and codes in addition to having certifications including:
Fire retardancy - In the United States, the common fire resistance rating certifications for commercial applications are NFPA 701 and California U.S. Title #19, which is the state’s public safety code requiring all commercial solar screen fabrics to be tested for minimum fire resistance standards. Internationally, the most common and acceptable standards for solar protection fabrics in Europe are M1 and B1 ratings. These fire ratings are far more stringent than NFPA 701.
Low VOC (Greenguard®) - This certification says that a product or material meets strict harmful chemical emissions limits. The Greenguard® Environmental Institute was founded to improve indoor air quality and reduce occupants' exposure to VOCs and other potentially harmful chemicals. The Greenguard ® Children and Schools Certification is enforces even more stringent emissions limits.
Reduction of Hazardous Substances - Another certification is RoHS, or Reduction of Hazardous Substances, which states that a product has been tested for heavy metals and is compliant.
Anti-microbial and fungal -The American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) publishes hundreds of technical standards including fabric rating tests for the growth of mold, mildew,bacteria , other types of fungi, etc. These ratings are especially important in healthcare projects.




In today’s buildings, products and materials must meet certain standards and codes in addition to having certifications including:
Fire retardancy - In the United States, the common fire resistance rating certifications for commercial applications are NFPA 701 and California U.S. Title #19, which is the state’s public safety code requiring all commercial solar screen fabrics to be tested for minimum fire resistance standards. Internationally, the most common and acceptable standards for solar protection fabrics in Europe are M1 and B1 ratings. These fire ratings are far more stringent than NFPA 701.
Low VOC (Greenguard®) - This certification says that a product or material meets strict harmful chemical emissions limits. The Greenguard® Environmental Institute was founded to improve indoor air quality and reduce occupants' exposure to VOCs and other potentially harmful chemicals. The Greenguard ® Children and Schools Certification is enforces even more stringent emissions limits.
Reduction of Hazardous Substances - Another certification is RoHS, or Reduction of Hazardous Substances, which states that a product has been tested for heavy metals and is compliant.
Anti-microbial and fungal -The American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) publishes hundreds of technical standards including fabric rating tests for the growth of mold, mildew,bacteria , other types of fungi, etc. These ratings are especially important in healthcare projects.




In today’s buildings, products and materials must meet certain standards and codes in addition to having certifications including:
Fire retardancy - In the United States, the common fire resistance rating certifications for commercial applications are NFPA 701 and California U.S. Title #19, which is the state’s public safety code requiring all commercial solar screen fabrics to be tested for minimum fire resistance standards. Internationally, the most common and acceptable standards for solar protection fabrics in Europe are M1 and B1 ratings. These fire ratings are far more stringent than NFPA 701.
Low VOC (Greenguard®) - This certification says that a product or material meets strict harmful chemical emissions limits. The Greenguard® Environmental Institute was founded to improve indoor air quality and reduce occupants' exposure to VOCs and other potentially harmful chemicals. The Greenguard ® Children and Schools Certification is enforces even more stringent emissions limits.
Reduction of Hazardous Substances - Another certification is RoHS, or Reduction of Hazardous Substances, which states that a product has been tested for heavy metals and is compliant.
Anti-microbial and fungal -The American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) publishes hundreds of technical standards including fabric rating tests for the growth of mold, mildew,bacteria , other types of fungi, etc. These ratings are especially important in healthcare projects.




In today’s buildings, products and materials must meet certain standards and codes in addition to having certifications including:
Fire retardancy - In the United States, the common fire resistance rating certifications for commercial applications are NFPA 701 and California U.S. Title #19, which is the state’s public safety code requiring all commercial solar screen fabrics to be tested for minimum fire resistance standards. Internationally, the most common and acceptable standards for solar protection fabrics in Europe are M1 and B1 ratings. These fire ratings are far more stringent than NFPA 701.
Low VOC (Greenguard®) - This certification says that a product or material meets strict harmful chemical emissions limits. The Greenguard® Environmental Institute was founded to improve indoor air quality and reduce occupants' exposure to VOCs and other potentially harmful chemicals. The Greenguard ® Children and Schools Certification is enforces even more stringent emissions limits.
Reduction of Hazardous Substances - Another certification is RoHS, or Reduction of Hazardous Substances, which states that a product has been tested for heavy metals and is compliant.
Anti-microbial and fungal -The American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) publishes hundreds of technical standards including fabric rating tests for the growth of mold, mildew,bacteria , other types of fungi, etc. These ratings are especially important in healthcare projects.




In today’s buildings, products and materials must meet certain standards and codes in addition to having certifications including:
Fire retardancy - In the United States, the common fire resistance rating certifications for commercial applications are NFPA 701 and California U.S. Title #19, which is the state’s public safety code requiring all commercial solar screen fabrics to be tested for minimum fire resistance standards. Internationally, the most common and acceptable standards for solar protection fabrics in Europe are M1 and B1 ratings. These fire ratings are far more stringent than NFPA 701.
Low VOC (Greenguard®) - This certification says that a product or material meets strict harmful chemical emissions limits. The Greenguard® Environmental Institute was founded to improve indoor air quality and reduce occupants' exposure to VOCs and other potentially harmful chemicals. The Greenguard ® Children and Schools Certification is enforces even more stringent emissions limits.
Reduction of Hazardous Substances - Another certification is RoHS, or Reduction of Hazardous Substances, which states that a product has been tested for heavy metals and is compliant.
Anti-microbial and fungal -The American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) publishes hundreds of technical standards including fabric rating tests for the growth of mold, mildew,bacteria , other types of fungi, etc. These ratings are especially important in healthcare projects.




How do I clean my fabrics?

Depending on the type of fabric, there are suggested methods for cleaning, including hand dusting, vacuuming with a soft brush attachment, or having the shades professionally cleaned. Please review the Window Treatment Cleaning and Maintenance Guides for specific instructions.

Depending on the type of fabric, there are suggested methods for cleaning, including hand dusting, vacuuming with a soft brush attachment, or having the shades professionally cleaned. Please review the Window Treatment Cleaning and Maintenance Guides for specific instructions.

Depending on the type of fabric, there are suggested methods for cleaning, including hand dusting, vacuuming with a soft brush attachment, or having the shades professionally cleaned. Please review the Window Treatment Cleaning and Maintenance Guides for specific instructions.

Depending on the type of fabric, there are suggested methods for cleaning, including hand dusting, vacuuming with a soft brush attachment, or having the shades professionally cleaned. Please review the Window Treatment Cleaning and Maintenance Guides for specific instructions.

Depending on the type of fabric, there are suggested methods for cleaning, including hand dusting, vacuuming with a soft brush attachment, or having the shades professionally cleaned. Please review the Window Treatment Cleaning and Maintenance Guides for specific instructions.
How can a fabric contribute to LEED?

The fabrics themselves can contribute to LEED certification points. The following credits can be affected by fabric selection:
Materials and Resources: One of the most sought-after credits within LEED Version 3 is within the Materials and Resources section, which encourages logical thinking about building products and materials. Fabrics made from pre- or post-consumer materials, like water bottles, can help achieve these points.
Daylight and Views: Another two credits within the Indoor Environmental Quality section encourage serious consideration about fabric selection and the use of automated shading to achieve a consistent natural light level to promote employee productivity.

The fabrics themselves can contribute to LEED certification points. The following credits can be affected by fabric selection:
Materials and Resources: One of the most sought-after credits within LEED Version 3 is within the Materials and Resources section, which encourages logical thinking about building products and materials. Fabrics made from pre- or post-consumer materials, like water bottles, can help achieve these points.
Daylight and Views: Another two credits within the Indoor Environmental Quality section encourage serious consideration about fabric selection and the use of automated shading to achieve a consistent natural light level to promote employee productivity.

The fabrics themselves can contribute to LEED certification points. The following credits can be affected by fabric selection:
Materials and Resources: One of the most sought-after credits within LEED Version 3 is within the Materials and Resources section, which encourages logical thinking about building products and materials. Fabrics made from pre- or post-consumer materials, like water bottles, can help achieve these points.
Daylight and Views: Another two credits within the Indoor Environmental Quality section encourage serious consideration about fabric selection and the use of automated shading to achieve a consistent natural light level to promote employee productivity.

The fabrics themselves can contribute to LEED certification points. The following credits can be affected by fabric selection:
Materials and Resources: One of the most sought-after credits within LEED Version 3 is within the Materials and Resources section, which encourages logical thinking about building products and materials. Fabrics made from pre- or post-consumer materials, like water bottles, can help achieve these points.
Daylight and Views: Another two credits within the Indoor Environmental Quality section encourage serious consideration about fabric selection and the use of automated shading to achieve a consistent natural light level to promote employee productivity.

The fabrics themselves can contribute to LEED certification points. The following credits can be affected by fabric selection:
Materials and Resources: One of the most sought-after credits within LEED Version 3 is within the Materials and Resources section, which encourages logical thinking about building products and materials. Fabrics made from pre- or post-consumer materials, like water bottles, can help achieve these points.
Daylight and Views: Another two credits within the Indoor Environmental Quality section encourage serious consideration about fabric selection and the use of automated shading to achieve a consistent natural light level to promote employee productivity.
How can I choose a fabric best suited for my project?
A project’s priorities, along with the functional needs for a given space, can help facilitate a fabric selection.
Commercially, fabric performance properties and certifications are equally as important as aesthetics. Priorities need to be established for each project. Priorities may include the aesthetic look of the fabric, energy savings potential, indoor environmental quality, preserving a view, blocking a view, and increasing privacy. These priorities help to eliminate or narrow down fabric options. Use the Performance Shading Advisor to help select the best solar screen fabric according to your project's parameters and priorities.
Residentially, fabrics election is most typically based on aesthetics and views. Choose a fabric that complements the décor of your space and gives you the degree of privacy according to the function of the interior space. A sheer fabric may be ideal for a kitchen or living-room application to allow for a view, while a translucent or blackout shade might be most appealing in a bedroom application.


A project’s priorities, along with the functional needs for a given space, can help facilitate a fabric selection.
Commercially, fabric performance properties and certifications are equally as important as aesthetics. Priorities need to be established for each project. Priorities may include the aesthetic look of the fabric, energy savings potential, indoor environmental quality, preserving a view, blocking a view, and increasing privacy. These priorities help to eliminate or narrow down fabric options. Use the Performance Shading Advisor to help select the best solar screen fabric according to your project's parameters and priorities.
Residentially, fabrics election is most typically based on aesthetics and views. Choose a fabric that complements the décor of your space and gives you the degree of privacy according to the function of the interior space. A sheer fabric may be ideal for a kitchen or living-room application to allow for a view, while a translucent or blackout shade might be most appealing in a bedroom application.
A project’s priorities, along with the functional needs for a given space, can help facilitate a fabric selection.
Commercially, fabric performance properties and certifications are equally as important as aesthetics. Priorities need to be established for each project. Priorities may include the aesthetic look of the fabric, energy savings potential, indoor environmental quality, preserving a view, blocking a view, and increasing privacy. These priorities help to eliminate or narrow down fabric options. Use the Performance Shading Advisor to help select the best solar screen fabric according to your project's parameters and priorities.
Residentially, fabrics election is most typically based on aesthetics and views. Choose a fabric that complements the décor of your space and gives you the degree of privacy according to the function of the interior space. A sheer fabric may be ideal for a kitchen or living-room application to allow for a view, while a translucent or blackout shade might be most appealing in a bedroom application.




A project’s priorities, along with the functional needs for a given space, can help facilitate a fabric selection.
Commercially, fabric performance properties and certifications are equally as important as aesthetics. Priorities need to be established for each project. Priorities may include the aesthetic look of the fabric, energy savings potential, indoor environmental quality, preserving a view, blocking a view, and increasing privacy. These priorities help to eliminate or narrow down fabric options. Use the Performance Shading Advisor to help select the best solar screen fabric according to your project's parameters and priorities.
Residentially, fabrics election is most typically based on aesthetics and views. Choose a fabric that complements the décor of your space and gives you the degree of privacy according to the function of the interior space. A sheer fabric may be ideal for a kitchen or living-room application to allow for a view, while a translucent or blackout shade might be most appealing in a bedroom application.
A project’s priorities, along with the functional needs for a given space, can help facilitate a fabric selection.
Commercially, fabric performance properties and certifications are equally as important as aesthetics. Priorities need to be established for each project. Priorities may include the aesthetic look of the fabric, energy savings potential, indoor environmental quality, preserving a view, blocking a view, and increasing privacy. These priorities help to eliminate or narrow down fabric options. Use the Performance Shading Advisor to help select the best solar screen fabric according to your project's parameters and priorities.
Residentially, fabrics election is most typically based on aesthetics and views. Choose a fabric that complements the décor of your space and gives you the degree of privacy according to the function of the interior space. A sheer fabric may be ideal for a kitchen or living-room application to allow for a view, while a translucent or blackout shade might be most appealing in a bedroom application.




How do I order fabric samples?

It is very easy to order fabric samples using this website. Simply add the fabric sample you wish to order to your sample cart, then place your free fabric sample order. You may order more than one fabric sample at a time (limit 10 per order). Once you fill out your contact information and submit your order, samples will typically arrive within 7-10 business days.

It is very easy to order fabric samples using this website. Simply add the fabric sample you wish to order to your sample cart, then place your free fabric sample order. You may order more than one fabric sample at a time (limit 10 per order). Once you fill out your contact information and submit your order, samples will typically arrive within 7-10 business days.

It is very easy to order fabric samples using this website. Simply add the fabric sample you wish to order to your sample cart, then place your free fabric sample order. You may order more than one fabric sample at a time (limit 10 per order). Once you fill out your contact information and submit your order, samples will typically arrive within 7-10 business days.

It is very easy to order fabric samples using this website. Simply add the fabric sample you wish to order to your sample cart, then place your free fabric sample order. You may order more than one fabric sample at a time (limit 10 per order). Once you fill out your contact information and submit your order, samples will typically arrive within 7-10 business days.

It is very easy to order fabric samples using this website. Simply add the fabric sample you wish to order to your sample cart, then place your free fabric sample order. You may order more than one fabric sample at a time (limit 10 per order). Once you fill out your contact information and submit your order, samples will typically arrive within 7-10 business days.
How do I place an order for Lutron shades?
We have Lutron representatives all over the world that can help with your next project. Locate a representative using our Where to Buy tool, or call Shades Customer Service at 1.800.446.1503.
We have Lutron representatives all over the world that can help with your next project. Locate a representative using our Where to Buy tool, or call Shades Customer Service at 1.800.446.1503.
We have Lutron representatives all over the world that can help with your next project. Locate a representative using our Where to Buy tool, or call Shades Customer Service at 1.800.446.1503.
We have Lutron representatives all over the world that can help with your next project. Locate a representative using our Where to Buy tool, or call Shades Customer Service at 1.800.446.1503.
We have Lutron representatives all over the world that can help with your next project. Locate a representative using our Where to Buy tool, or call Shades Customer Service at 1.800.446.1503.
What type of shades should I choose?

Automated shades can make any space more comfortable and energy-efficient. With over 20 years of experience and knowledge in the automated shading industry, Lutron is the world leader in precision-controlled automated shades.
Lutron also offers a wide variety of shading options, allowing you to create a cost-effective, environmentally-friendly, and aesthetically pleasing solution. Depending on the factors that are most important to you, you can select fabrics that increase daylight harvesting ability, reduce electric light consumption, minimize glare, enhance comfort, and improve productivity.
By maximizing energy efficiency, daylight and views, as well as incorporating environmentally-friendly materials, automated shades can help your building meet and exceed building codes and standards such as ASHRAE and LEED.

Automated shades can make any space more comfortable and energy-efficient. With over 20 years of experience and knowledge in the automated shading industry, Lutron is the world leader in precision-controlled automated shades.
Lutron also offers a wide variety of shading options, allowing you to create a cost-effective, environmentally-friendly, and aesthetically pleasing solution. Depending on the factors that are most important to you, you can select fabrics that increase daylight harvesting ability, reduce electric light consumption, minimize glare, enhance comfort, and improve productivity.
By maximizing energy efficiency, daylight and views, as well as incorporating environmentally-friendly materials, automated shades can help your building meet and exceed building codes and standards such as ASHRAE and LEED.

Automated shades can make any space more comfortable and energy-efficient. With over 20 years of experience and knowledge in the automated shading industry, Lutron is the world leader in precision-controlled automated shades.
Lutron also offers a wide variety of shading options, allowing you to create a cost-effective, environmentally-friendly, and aesthetically pleasing solution. Depending on the factors that are most important to you, you can select fabrics that increase daylight harvesting ability, reduce electric light consumption, minimize glare, enhance comfort, and improve productivity.
By maximizing energy efficiency, daylight and views, as well as incorporating environmentally-friendly materials, automated shades can help your building meet and exceed building codes and standards such as ASHRAE and LEED.

Automated shades can make any space more comfortable and energy-efficient. With over 20 years of experience and knowledge in the automated shading industry, Lutron is the world leader in precision-controlled automated shades.
Lutron also offers a wide variety of shading options, allowing you to create a cost-effective, environmentally-friendly, and aesthetically pleasing solution. Depending on the factors that are most important to you, you can select fabrics that increase daylight harvesting ability, reduce electric light consumption, minimize glare, enhance comfort, and improve productivity.
By maximizing energy efficiency, daylight and views, as well as incorporating environmentally-friendly materials, automated shades can help your building meet and exceed building codes and standards such as ASHRAE and LEED.

Automated shades can make any space more comfortable and energy-efficient. With over 20 years of experience and knowledge in the automated shading industry, Lutron is the world leader in precision-controlled automated shades.
Lutron also offers a wide variety of shading options, allowing you to create a cost-effective, environmentally-friendly, and aesthetically pleasing solution. Depending on the factors that are most important to you, you can select fabrics that increase daylight harvesting ability, reduce electric light consumption, minimize glare, enhance comfort, and improve productivity.
By maximizing energy efficiency, daylight and views, as well as incorporating environmentally-friendly materials, automated shades can help your building meet and exceed building codes and standards such as ASHRAE and LEED.